FREE SHIPPING FOR ORDERS R500 OR MORE
FREE SHIPPING FOR ORDERS R500 OR MORE

PCOS Treatment
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder in women during their reproductive years and the single most common cause of infertility in women.
InsuMax-Q
Home | Product Ranges | PCOS Assistance

Nappi Code: 723593001
Bar Code: 6009880503087
incl. 15% VAT
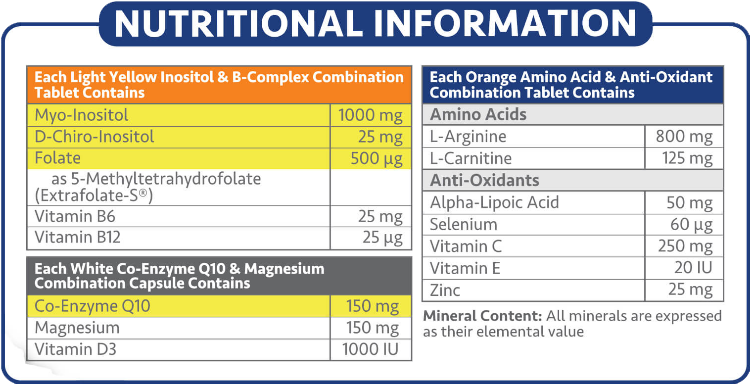
Each InsuMax-Q pack contains a 30-day supply of the 3 Components:
- 30 x Inositol and B-Complex Combination Tablets
- 30 x Coenzyme Q10 and Magnesium Combination Capsules
- 30 x Amino Acid and Antioxidant Combination Tablets
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) has become an increasingly prevalent condition in young females. PCOS can seem to be a collection of unrelated symptoms affecting your menstrual cycle, fertility, appearance, and weight. But when you piece the puzzle of PCOS together, you can see how the symptoms can relate to one another and how simple lifestyle changes can have a positive impact on them. Unlike many disorders, you are able to improve PCOS by implementing the correct measures to manage the causes. Recognising the symptoms of PCOS early and working on improving Insulin Resistance through diet and exercise can help prevent complications of PCOS, including infertility.
PCOS is described as a syndrome rather than a disease because it shows up as a group of signs and symptoms that can occur in any combination. This group of symptoms mainly affect the ovaries and ovulation. The three main features of PCOS are:
- multiple cysts forming in the ovaries
- high levels of male hormones
- irregular or skipped menstrual cycles
The exact causes of all types of PCOS are not fully known or understood. It is believed that high levels of male hormones prevent the ovaries from producing hormones and making eggs normally. This means that the causes of PCOS are not the same for every woman. Genes, insulin resistance, and inflammation have all been linked to excess androgen production and may be underlying causes of PCOS.
PCOS Symptoms:
- Abnormal menstrual cycle: When you have PCOS your periods may be heavier, lighter, irregular, or absent altogether. However, you may have completely normal periods and still have PCOS.
- Weight gain: In women with PCOS, weight gain is mostly due to high levels of insulin circulating in the blood. Cells normally absorb glucose with the help of insulin. When cells don’t respond normally to insulin, your body produces even more insulin, to “force” the cells into responding. When insulin levels rise, other hormonal changes can lead to increased appetite and decreased fat burning, which lead to weight gain.
- Acne and oily skin: Women with PCOS tend to have higher levels of androgens which cause acne and increased skin oiliness.
- Excess hair growth: Your body may be hairier in places such as your chest, thighs, face, and back, as a side effect of androgens.
- Hair loss: The hair on your head may thin if you have PCOS, another side effect of higher androgen levels.
- Sleep problems and fatigue or exhaustion: These symptoms can be due to fluctuating hormone levels and increased anxiety.
- Depression, anxiety, irritability, and mood swings: These symptoms are probably due to disrupted hormone levels.
- Fertility problems: The hormonal imbalances that come with PCOS can disrupt or even prevent ovulation.
- Metabolic syndrome: Also known as Syndrome X, Metabolic Syndrome is a cluster of symptoms, including Insulin Resistance (where insulin produced by the body doesn’t work efficiently), high blood pressure, and high cholesterol. It can lead to diabetes and heart disease.
PCOS Treatment in South Africa
There is no “silver bullet solution” for PCOS. PCOS requires a multidimensional approach to its management. This approach starts with a:
- Diet Plan
- Exercise Plan
- Vitamin and Mineral Supplementation
- Healthcare Professional Care (Gynaecologist / OBGYN / Endocrinologist)
If you’re willing to relook at your diet and start a simple exercise programme, you can gain a great deal of control over your PCOS symptoms. Insulin resistance causes many PCOS symptoms, and diet and exercise help control Insulin Resistance.
When it comes to the best supplements for PCOS, we can recommend the use of the nutritional supplement InsuMax-Q. InsuMax-Q contains a combination of well-known vitamins and minerals that have shown effectiveness in assisting in the balancing of hormones and the management of PCOS. It is the accumulative effect of all these nutrients that assist in PCOS. And not just one specific vitamin or mineral.
InsuMax-Q contains Myo-Inositol and D-Chiro Inositol in a 40:1 ratio which mimics the plasma physiological ratio of these nutrients in the cells required for aiding the fight against Insulin Resistance. Myo-Inositol and D-Chiro Inositol in a 40:1 ratio is the recommended ratio for balancing hormones and relieving Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) symptoms. Using Myo-Inositol and D-Chiro Inositol in a 40:1 ratio may decrease the time taken to get results compared to using Myo-Inositol alone, and it also lowers the dosage of Myo-Inositol required. Myo-Inositol is an insulin sensitiser and is involved in cellular glucose uptake. D-Chiro Inositol is an insulin sensitiser and is involved in glycogen synthesis.
Coenzyme Q10 is a powerful Antioxidant which plays a critical role in intracellular energy production in the mitochondria (ATP production)
Vitamin D plays a key role in glucose regulation, notably in decreasing Insulin Resistance. Low levels of Vitamin D have been negatively correlated with the incidence of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes

Take one Yellow Tablet in the Morning with Breakfast
Take one White Capsule at Night with Dinner
Take one Orange Tablet at Night with Dinner





Frequently asked Questions about PCOS Treatment
Metabolic Syndrome is a medical term for a group of risk factors namely high blood pressure, high blood sugar, unhealthy cholesterol levels, and abdominal fat. The symptoms of Metabolic Syndrome would be any three or more of these risk factors together.
To be diagnosed with Metabolic Syndrome you need to present with three or more of the following characteristics (this also includes if you are taking medication to manage any one of these characteristics):
Abdominal Obesity
High Triglyceride Level
Low HDL Cholesterol Level
High Blood Pressure
High Fasting Blood Sugar
When a person has Metabolic Syndrome, it can be an overall indication of an unhealthy lifestyle which can be caused by:
Obesity
An inactive lifestyle
Insulin resistance
Age – your risk goes up as you get older
Genetics – ethnicity and family history
Insulin Resistance is characterised by abnormal high levels of the hormone Insulin found in the blood. The cells in your muscles, fat, and liver don’t respond well to Insulin and can’t use glucose from your blood for energy. To compensate for this your pancreas makes more Insulin and eventually your blood sugar levels will rise.
Under normal circumstances Insulin rises briefly after eating a meal as the body’s response to Glucose Metabolism. The liver and muscles are stimulated to take up sugar from the blood and convert it to energy. That will then cause blood sugar levels and blood Insulin levels to decrease. With normal insulin sensitivity, both sugar and Insulin levels will appear normal on a fasting blood Glucose Test.
When someone has Insulin Resistance, their blood sugar levels may be normal, but their blood Insulin levels are high. The pancreas oversecretes Insulin to try and get its message through to the cells of the body to function. Too much Insulin generates inflammation and causes weight gain which can lead to Type 2 Diabetes and heart disease.
Excess Insulin is also an underlying physiological driver of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
You will not be able to tell that you have Insulin Resistance by the way you feel. You’ll need to get a blood test that checks your blood sugar and Insulin levels.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is the most common endocrine disorder in women during their reproductive years and the single most common cause of infertility in women. The main features of PCOS include hyperandrogenism, ovulatory dysfunction and polycystic ovarian morphology.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) seems to be a collection of unrelated symptoms affecting your menstrual cycle, fertility, appearance, and weight. Unlike many disorders, you are able to improve PCOS by implementing the correct measures to manage the causes. Recognizing the symptoms of PCOS early and working on improving insulin resistance through diet and exercise can help prevent complications of PCOS, including infertility.
PCOS is described as a syndrome rather than a disease because it shows up as a group of signs and symptoms that can occur in any combination.
Doctors don’t know exactly what causes PCOS. They believe that high levels of male hormones prevent the ovaries from producing hormones and making eggs normally.
Genes, insulin resistance, and inflammation have all been linked to excess androgen production.
No, Insulin Resistance and Diabetes are not the same. When you have Insulin Resistance, your pancreas needs to make extra Insulin. For a while, this will work, and your blood sugar levels will stay normal. Over time, your pancreas won’t be able to keep up. If you don’t make changes in the way you eat and exercise, your blood sugar levels will rise until you have prediabetes. If you can’t manage prediabetes, you could be diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes later.
Insulin Resistance is characterised by abnormally high levels of Insulin found in the blood.
Under normal circumstances Insulin rises briefly after eating a meal as the body’s response to Glucose Metabolism. The liver and muscles are stimulated to take up sugar from the blood and convert it to energy. That will then cause blood sugar levels and blood Insulin levels to decrease. With normal insulin sensitivity, both sugar and Insulin levels will appear normal on a fasting blood Glucose Test.
When someone has Insulin Resistance, their blood sugar levels may be normal, but their blood Insulin levels are high. The pancreas oversecretes Insulin to try get its message through to the cells of the body to function. Too much Insulin generates inflammation and causes weight gain which can lead to Type 2 Diabetes and heart disease.
You will not be able to tell that you have Insulin Resistance by the way you feel. You’ll need to get a blood test that checks your blood sugar and Insulin levels.
Some signs of Insulin Resistance include:
- A waistline over 101.6 cm in men and 88.9 cm in women
- Blood pressure readings of 130/80 or higher
- A fasting glucose level over 100 mg/dL
- A fasting triglyceride level over 150 mg/dL
- An HDL cholesterol level under 40 mg/dL in men and 50 mg/dL in women





























